Accepted publications in IEEE Magazine and Transactions
About
We're delighted to share that two papers by our group have been accepted for publication, one in IEEE Wireless Communications Magazine and another in IEEE Transactions on Communications.
Paper 1: Distributed Integrated Sensing, Localization, and Communications over LEO Satellite Constellations
📄 Free access (arXiv): https://lnkd.in/enYmfenC
📃 IEEE Xplore: Distributed Integrated Sensing, Localization, and Communications Over LEO Satellite Constellations | IEEE Journals & Magazine | IEEE Xplore
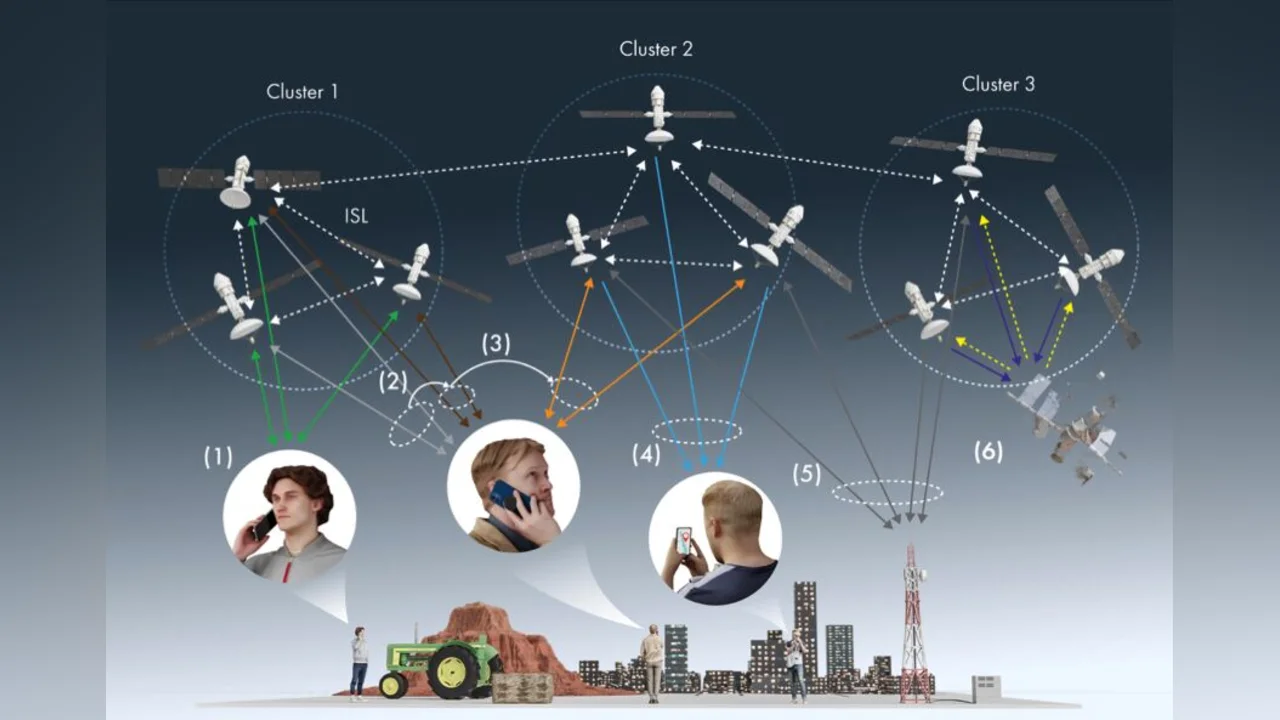
LEO constellations are rapidly evolving from “connectivity-only” platforms into multi-functional space networks. In this article, we introduce DISLAC — distributed integrated sensing, localization, and communications — where multiple LEO satellites cooperate via inter-satellite links (ISLs) to jointly boost throughput, positioning accuracy, and sensing robustness.
🔑 What we cover (high level):
✅ A constellation-level DISLAC framework (communication + localization + sensing) enabled by ISLs
✅ Case studies on multi-LEO cooperative beamforming, delay/Doppler-aware positioning, and OFDM trade-offs for multistatic sensing
✅ Key practical considerations (e.g., synchronization, antenna/RF-chain flexibility, ISL/topology constraints) + open research directions
🙏 Many thanks to my amazing collaborators across 6 institutions, spanning both academia and industry! This cross-institution teamwork made the study possible and genuinely enjoyable😊
Paper 2: Positioning-Aided Channel Estimation for Multi-LEO Satellite Cooperative Beamforming, published in IEEE Transactions on Communications! 📡🛰️
🌍 Accurate CSI acquisition is one of the key bottlenecks in LEO satellite communications, due to severe link budgets, high mobility, and synchronization imperfections. In this work, we show that positioning is not just a service, but a powerful enabler for communication in future non-terrestrial networks.
💡 Highlights:
⭐ Two-timescale PACE framework: We propose a positioning-aided channel estimation (PACE) framework that exploits the distinct timescales of geometry-related parameters and fast channel gains in LEO systems.
⭐ Rigorous performance analysis: Using misspecified Cramér–Rao bounds (MCRB), we quantify how practical impairments, such as inter-satellite clock bias and CFO, impact both positioning and channel estimation accuracy.
⭐ Multi-LEO cooperative beamforming: Leveraging PACE-estimated CSI, we design a low-complexity WMMSE-based cooperative beamforming strategy that mitigates single-satellite link budget limitations and boosts downlink performance.